Measurement & scaling


Rapid‐guessing behavior: Its identification, interpretation, and implications
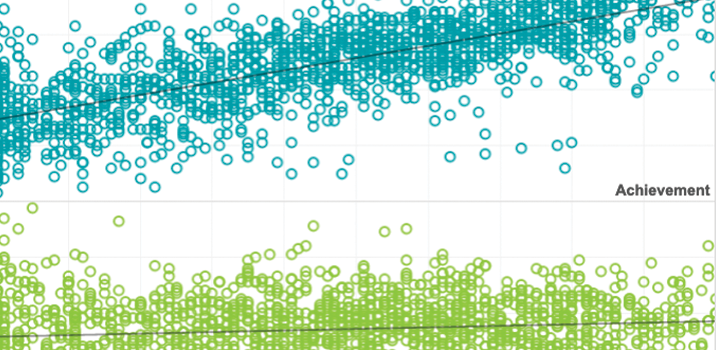
The rise of computer‐based testing has brought with it the capability to measure more aspects of a test event than simply the answers selected or constructed by the test taker. One behavior that has drawn much research interest is the time test takers spend responding to individual multiple‐choice items.
By: Steven Wise
Topics: Measurement & scaling, Innovations in reporting & assessment, School & test engagement


Robust IRT scaling: Considerations in constructing item bank from tests across years
This study investigates the impact of three different IRT scaling and equating methods in building an item bank of tests from 23 years of a national licensure exam . The study focuses on several key psychometric issues including scaledriftandequatingerrors.
By: Jungnam Kim, Dong-In Kim, Furong Gao
Topics: Measurement & scaling, Computer adaptive testing, Item response theory


When computer-based tests are used, disengagement can be detected through occurrences of rapid-guessing behavior. This empirical study investigated the impact of a new effort monitoring feature that can detect rapid guessing, as it occurs, and notify proctors that a test taker has become disengaged.
By: Steven Wise, Megan Kuhfeld, James Soland
Topics: Measurement & scaling, Innovations in reporting & assessment, School & test engagement


Identifying disengaged survey responses: New evidence using response time metadata
In this study, we condition results from a variety of detection methods used to identify disengaged survey responses on response times. We then show how this conditional approach may be useful in identifying where to set response time thresholds for survey items, as well as in avoiding misclassification when using other detection methods.
By: James Soland, Steven Wise, Lingyun Gao


This paper briefly discusses the trade-offs involved in making such a transition, and then focuses on a relatively unexplored benefit of computer-based tests – the control of construct-irrelevant factors that can threaten test score validity.
By: Steven Wise
Topics: Measurement & scaling, Innovations in reporting & assessment, School & test engagement


Predicting time to reclassification for English learners: A joint modeling approach
The development of academic English proficiency and the time it takes to reclassify to fluent English proficient status are key issues in English learner (EL) policy. This article develops a shared random effects model (SREM) to estimate English proficiency development and time to reclassification simultaneously, treating student-specific random effects as latent covariates in the time to reclassification model.
By: Tyler Matta, James Soland


A Tech Refresh for Reading Fluency
In this Ed Tech Digest article, Cindy Jiban discusses how oral reading fluency assessment is now commonplace in the primary grades. This represents a significant step for data-based problem solving in education. However, given some of the side effects that have emerged, it is clear that fluency assessment is due for significant structural improvement.
Topics: Measurement & scaling, Academic content, Reading & language arts