Journal article
Rethinking summer slide: The more you gain, the more you lose
2019
By: Megan Kuhfeld

Abstract
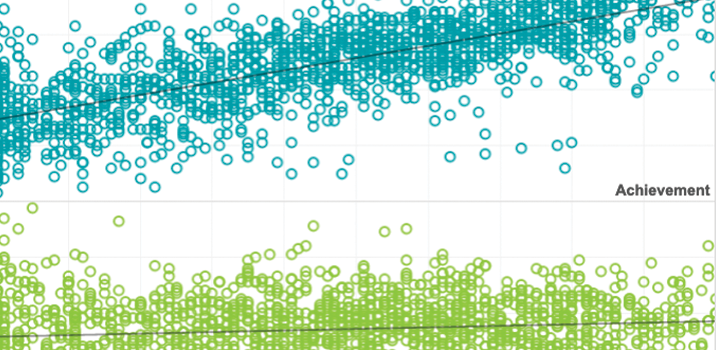
It has been common knowledge for decades that poor and working-class students tend to experience “summer learning loss,” a drop in performance between spring and fall that serves to widen the gap between students. However, new research shows that the reality of summer learning loss is more complex. Megan Kuhfeld draws on data from the 3.4 million students who took the NWEA MAP Growth assessments to find that summer slide is common, but not inevitable. According to the data, the students who experienced the greatest loss were those who made the greatest gains during the previous school year. The research also calls into question about the usual explanations for learning loss, such as access to summer programs and length of the school year.
See MoreThis article was published outside of NWEA. The full text can be found at the link above.
Associated Research
Related Topics


Family engagement as a long-term strategy for continued COVID recovery
This NWEA research report emphasizes the vital role of family engagement in helping students recover academically from the disruptions of the COVID-19 pandemic. The report synthesizes current research on family engagement, examines the effectiveness of current strategies, identifies common barriers, and offers guidance for how districts can communicate more effectively with families about student progress.
By: Ayesha K. Hashim, Rebecca Johnson, Rachel Perera
Topics: COVID-19 & schools, Equity, Growth, Guidance


Boys regain the advantage in middle school STEM skills: Post-COVID trends in gender achievement gaps
The research study used a robust set of data from three national assessments to examine trends in gender gaps in 8th grade STEM skills over the course of the pandemic.
By: Megan Kuhfeld, Karyn Lewis, Gustave Robinson
Products: MAP Growth
Topics: COVID-19 & schools, Equity, Growth, Math & STEM


This is the accompanying technical appendix to the research study, “Boys regain the advantage in middle school STEM skills: Post-COVID trends in gender achievement gaps,” leveraging data from three national assessments, as well as enrollment in Algebra, to examine trends in gender gaps in 8th grade STEM skills over the course of the pandemic.
By: Megan Kuhfeld, Karyn Lewis, Gustave Robinson
Products: MAP Growth
Topics: COVID-19 & schools, Equity, Growth, Math & STEM


Integrating Literacy and Science: A Powerful Partnership for Student Success
This research brief explores the connection between science and literacy instruction documenting the benefits of integrated science and literacy instruction at the elementary level, and highlighting the benefits of integrating instruction while providing research-based guidance on how to effectively do this.
By: Susan Kowalski, Ayesha K. Hashim, Scott J. Peters
Topics: Growth, Equity, Informing instruction, Math & STEM


Practitioner’s Guide to Integrating Literacy and Science
This is the accompanying guide to the research brief, Integrating Literacy and Science: A Powerful Partnership for Student Success, which describes four key components of effective integration of literacy and science instruction at the elementary level. In this practitioner’s guide, we provide sample lessons to demonstrate each of these components in action in an elementary classroom.
By: Scott J. Peters, Susan Kowalski, Ayesha K. Hashim
Products: MAP Growth
Topics: Equity, Growth, Informing instruction, Math & STEM


COVID’s impact on science achievement: Trends from 2019 through 2024
This new report examines the pandemic’s impacts on academic achievement and gain in Science and continues ongoing research by NWEA® analyzing the degree to which the COVID-19 pandemic, and its associated school closures, influenced student learning.
By: Susan Kowalski, Scott J. Peters, Megan Kuhfeld, Gustave Robinson, Karyn Lewis
Products: MAP Growth
Topics: COVID-19 & schools, Equity, Growth


Technical Brief – COVID’s impact on science achievement: Trends from 2019 through 2024
This is the accompanying technical brief to the new report (Covid’s impact on science achievement: Trends from 2019 through 2024) that examines the pandemic’s impacts on academic achievement and gain in Science and continues ongoing research by NWEA® analyzing the degree to which the COVID-19 pandemic, and its associated school closures, influenced student learning.
By: Susan Kowalski, Scott J. Peters, Megan Kuhfeld, Gustave Robinson, Karyn Lewis
Products: MAP Growth
Topics: COVID-19 & schools, Equity, Growth