Research brief
English Language Learners, self-efficacy, and the achievement gap
2019
By: James Soland

Description
Learn more about the relationship between self-efficacy and the persistence of achievement gaps for English Language Learners.
View research briefAssociated Research
Related Topics

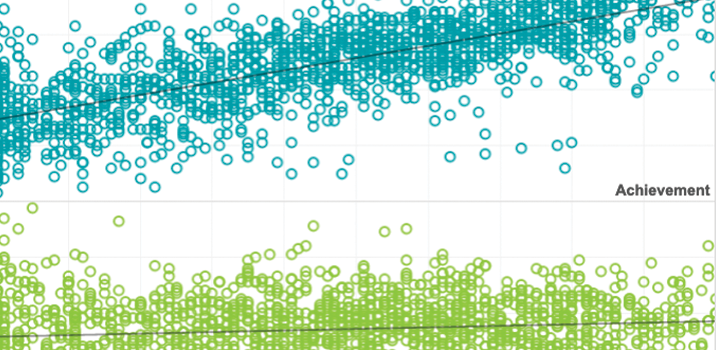
Do high flyers maintain their altitude?
In the visualizations in this exhibit, you can compare the performance and growth of various groups of high achievers to that of their peers over multiple years.
By: Yun Xiang, Michael Dahlin, John Cronin, Robert Theaker, Sarah Durant
Topics: Equity, High-growth schools & practices


A level playing field: College readiness standards
Some of our assumptions about the growth and performance of students from high-poverty schools relative to their peers from wealthier schools may be challenged in this data gallery, where you can explore how school poverty level interacts with student growth, college readiness, and college access.
By: Michael Dahlin, Beth Tarasawa
Topics: Equity, College & career readiness


A level playing field: College readiness standards
This study examines the academic growth of 35,000 elementary and middle school students in 31 states—all of them high achievers within their own schools—over a three-year period.
By: Michael Dahlin, Beth Tarasawa
Topics: Equity, College & career readiness


Do high flyers maintain their altitude? Performance trends of top students
In this study from the Thomas B. Fordham Institute, achievement trends from NWEA’s longitudinal growth database were used to track students who scored at or above the 90th percentile on this assessment in order to see if they maintained their high achievement.
By: Yun Xiang, Michael Dahlin, John Cronin, Robert Theaker, Sarah Durant
Topics: Equity, High-growth schools & practices


Increasing parental involvement of English language learner families: What the research says
The nearly 10 million English Language Learners (ELLs) represent the fastest-growing segment of the US’s public school student population. While research continually finds that ELL parents, generally speaking, place a high value on their children’s education, many immigrant, refugee, and ELL parents experience their relationships with their children’s schools very differently from mainstream English-speaking families.
By: Beth Tarasawa, Jacqueline Waggoner


What does equity and accessibility look like within assessment?
Creating tests and items from the beginning with Universal Design for Learning in mind, removing barriers by adding alt-tags, and incorporating more culturally rich materials are all steps NWEA is doing to improve our equity for all students.
By: Elizabeth Barker
Topics: Equity, Accessibility


NWEA promotes accessibility in assessment with release of image description guidelines
Image descriptions are important to make computer-based assessments accessible to students using assistive technology (AT) devices, such as screen readers and refreshable braille displays. NWEA, with support from the National Center for Accessible Media (NCAM), has created guidelines for describing many variations of images, charts, and graphics targeted specifically to the disciplines of reading, language usage, science, and mathematics.
By: Elizabeth Barker
Topics: Equity, Accessibility