Does four equal five? Implementation and outcomes of the four-day school week
The four-day school week (4dsw) is growing in popularity, especially in rural areas across the western United States. RAND researchers conducted a study of the implementation and outcomes of the 4dsw in numerous districts across Idaho, New Mexico, and Oklahoma, as well as administrative data from these and other states. The analyses resulted in mixed findings, with small cost savings and high satisfaction for teachers, families, and students, but lower test scores related to the 4dsw. Given these mixed findings, communities are likely to make different choices about the 4dsw depending on their goals and the local context.
By: M. Rebecca Kilburn, Andrea Phillips, Celia Gomez, Louis Mariano, Christopher Doss, Wendy Troxel, Emily Morton, Kevin Estes
Topics: Informing instruction


Family perceptions of participating in a structured summer kindergarten transition program
Researchers interviewed parents whose children participated in a three-week structured kindergarten transition program designed to promote parental involvement in school, reduce students’ chronic absenteeism, and increase children’s readiness for kindergarten. Interviewees expressed that participating in the program yielded benefits for themselves and their children, and proposed various ways that adjusting the program could better meet the needs of all stakeholders. Parent suggestions were synthesized into multiple implications for practice and substantiated by current relevant literature.
By: Christopher Merideth, Beth Cavanaugh, Sue Romas, Nicole Ralston, Eva Arias, Beth Tarasawa, Jacqueline Waggoner
Topics: Early learning, Empowering educators


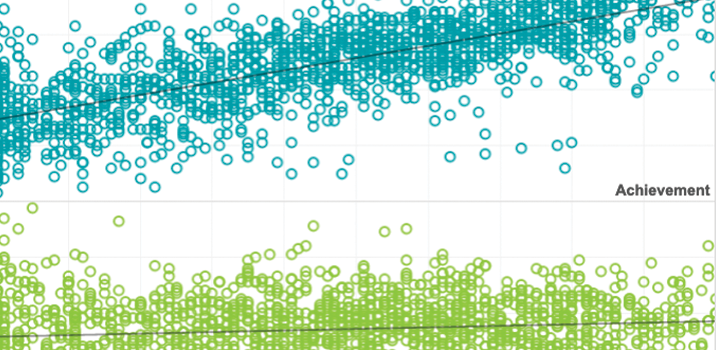
How does schooling affect inequality in students’ academic skills? This study uses seasonal comparisons to examine the possibilities that schooling exacerbates, reduces, or reproduces overall skill inequality in math, reading, language use, and science with recent national data on US public school students spanning numerous grade levels from the NWEA MAP Growth assessment. Results suggest that schooling has a compensatory effect on inequality in reading, language, and science skills but not math skills. Theoretical implications of findings are discussed.
By: Dennis Condron, Douglas Downery, Megan Kuhfeld


Disparities and discrimination in student discipline by race and family income
Black and poor students are suspended from U.S. schools at higher rates than White and nonpoor students. While the existence of these disparities has been clear, the causes have not. By comparing the punishments given to Black and White (or poor and nonpoor) students who fight one another, the study addresses a challenge that has kept prior studies from identifying discrimination in student discipline. It finds that Black and poor students are punished more harshly than the students with whom they fight.
By: Nathan Barrett, Andrew McEachin, Jonathan Mills, Jon Valant
Topics: Equity


Six insights regarding test-taking disengagement
There has been increasing concern about the presence of disengaged test taking in international assessment programs and its implications for the validity of inferences made regarding a country’s level of educational attainment. In this paper, the author discusses six important insights yielded by 20 years of research on this and implications for assessment programs.
By: Steven Wise


Predictors and consequences of school mobility in middle childhood
This study examined family factors associated with school mobility and if either a move during the previous year or cumulative moves across elementary school were related to child functioning. School mobility during elementary school did not appear to be a pervasive risk although the authors were unable to study very high rates of school mobility because of very small sample sizes.
By: Deborah Lowe Vandell, Megan Kuhfeld, Elizabeth Gershoff, Robert Crosnoe
Topics: Middle school, Social-emotional learning


MAP Reading Fluency theory of action
The MAP Reading Fluency theory of action shows the hypothesized mechanisms of change and intermediate goals leading to the overarching goal of helping all students read fluently with comprehension.
By: Mary Ann Simpson
Products: MAP Reading Fluency
Topics: Equity, Measurement & scaling